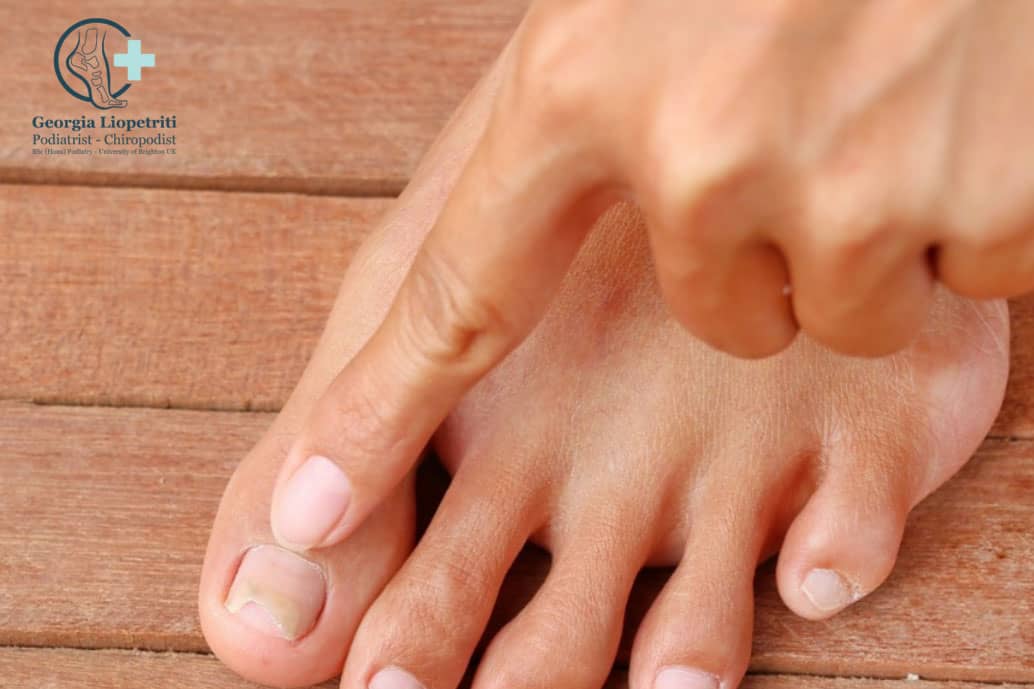
Onychomycosis is the fungal infection of the nail plate and although it is not considered harmful, it is stressful for many people and can spread to the nail matrix and other toes if left untreated. Once the infection has attacked the nail root, the fungus can permanantly damage the nail.
What are fungal nails?
What causes fungal nails?
A number of fungi can cause fungal nail, the most common culprit is a dermatophyte called trichophyton rubrum. Podiatrists often do a nail culture test to see if a nail is fungal, and what kind of fungus it is.
Fungi thrive in warm, moist dark environments, therefore footwear – particularly trainers – provide the perfect breeding ground. The big toe nail is most commonly affected.
Who gets fungal nails?
Anyone can contract a fungal nail infection, however some people are more at risk of fungal nails than others, and these include:
Older people (over 55) and Children
People with diabetes ( twice as common)
People with sweaty feet
Athletes and people who frequent gyms and swimming pools
People who live with someone who has a fungal nail
People with athlete’s foot
People who have a nail that has been damaged
People with psoriasis
People who have a weakened immune system
People with peripheral vascular disease (poor circulation)
What are the signs and symptoms of fungal nails?
The signs of a fungal nail vary, but may include:
Thickened nails
Discoloured nails
Debris beneath the nail plate
Cracks in the nail
Types of fungal nails:
Benefits of podiatry for fungal nails
The Podiatrist can advise you on treatment, as well as provide information and advice on how to prevent the infection from either spreading or recurring. If nails are thickened your podiatrist can thin the nail/s making them less unsightly. Thinning the nail will also allow any topical antifungals to penetrate the nail; making treatment more effective.
What would podiatry for fungal nails involve?
Following assessment, this will include taking down a medical history as well as a history of the problem. This information along with examination of the affected nail/s and an assessment of the foot will enable the podiatrist to reach a diagnosis.
There are a number of treatments for fungal nails, this is dependent upon the extent of the infection and the individual patient.
It is important to remember that the treatment of fungal nail takes time and patience. This is because it takes a lot of time for new, uninfected nail to grow through. If the whole nail is infected, this can take up to one year.